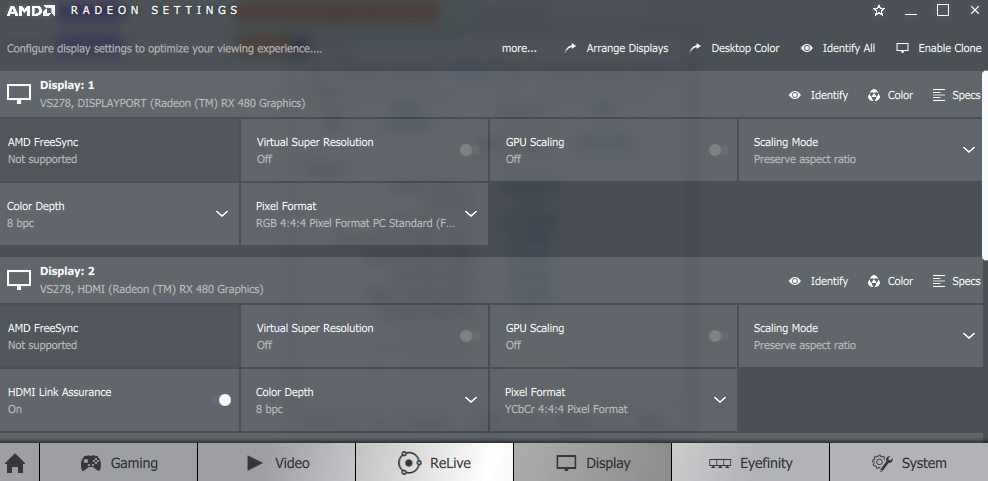
High resolution, increased contrast, and smoother playback mean that computer graphics become vivd and more realistic. In most cases, the situation is similar. If you watch a basketball game and the point guards appear as the protective gear on the football field, the image is likely been stretched and has the wrong aspect ratio. What is AMD GPU scaling is one way to avoid this problem.
Table of Contents
What is AMD GPU Scaling Graphics Driver?
If you go to the driver settings for the AMD Radeon graphics card, in the Display parameters section, you will find the “GPU Scaling” option. Nvidia also has this option, calling it a little different. By default, this setting is always enabled. But why is it necessary, and when should it be turned on?
Also Read: Can’t open NVidia control panel.
What is AMD GPU Scaling for?
We need this option to automatically adjust the resolution of the image displayed on this or that application monitor. For example, when you start a particular game, by default, it has a resolution and aspect ratio and your monitor may not support it.
The video card driver corrects this situation with the scaling option turned on at the GPU level and optimizes the image output to the maximum, so there are no errors about unsupported mode on the monitor or any black bars on the sides of the screen.
Basics of AMD GPU Scaling
GPU scaling is an option available in the configuration menu of many GPUs. A graphics processor is a computer processor designed specifically to create on-screen images that are especially useful when playing videos and games.
GPU scaling eliminates the inconsistency of the image the width of the image relative to its height — between the image created by the computer program, such as a software application or game, and the screen resolution.
GPU scaling is commonly used to get the results of an older video game designed for an era when most computer displays use a 4: 3 aspect ratio and transforms it so it fits nicely into the screen.
General parameters of AMD GPU scaling
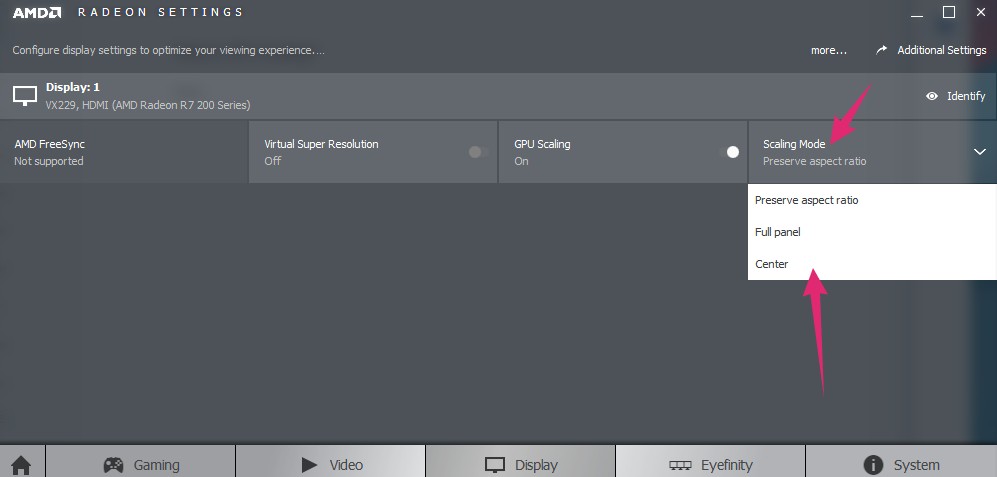
Although the exact parameters vary from GPU to GPU, the three scaling methods available on many AMD GPUs are good examples of common solutions. The “Keep Inspect Ratio” adds black bars at the top, bottom, left, or right of the image, filling the screen without expanding the image.
“Scale image to full panel size” The image is stretched until it fills the screen, so it does not waste space, but the image may look awkward.
If there is an image smaller than the screen resolution, “Use centered timings” is ideal; This option does not scale the image but places it in the center of the screen and with black stripes on all sides.
Underscan/Overscan
Depending on the screen, video source, and GPU, you may see black bars around the image when you did not expect that image to be cropped because it extends beyond the edges of the screen. This is the mismatch between analyzing and scaling your GPU image.
Most GPUs have a quick fix option called ” Underscan/Overscan” or something similar in the configuration menu. Under this, we can do scaling as usual with the Underscan/Overscan option. Additionally, we can shrink the image or expand it to get the desired fit.
Also Read: What Is A Normal CPU Temp While Gaming?
Input delay
Using scaling with a GPU requires more processing than displaying the image as it is, hence processing takes longer. Often the extra time is only a fraction of a second, and there is no noticeable difference when playing a video.
However, if you are playing games, you will notice that the delay is noticeable and causes a delay in the input where there is a delay between pressing the button and the action that appears on the screen hamper your ability to act quickly in the game. In this case, compare the effects of the input delay with the non-scaling effect of the image.
When should I start AMD GPU scaling?
You should enable this when sending a signal to the monitor in an unsupported format where you have trouble starting games, or if the monitor image is not in full screen and has black bars at the top and/or sides.