OLED Stands for Organic-light radiating diode while AMOLED Stands for the Active Matrix Organic light-transmitting diode. These two are the screen show. We will analyze both the screen display and discover the benefits of both the Screen types and afterward we finish up the better showcase for your cell phone, AMOLED vs OLED vs LCD.
AMOLED Is a Type of OLED. The upside of the AMOLED Over OLED is that it offers no limitation on the screen size. AMOLED Screen has a TFT Capacitor while OLED Screen contains a LED, it has a natural material that discharges light when current is given to it.
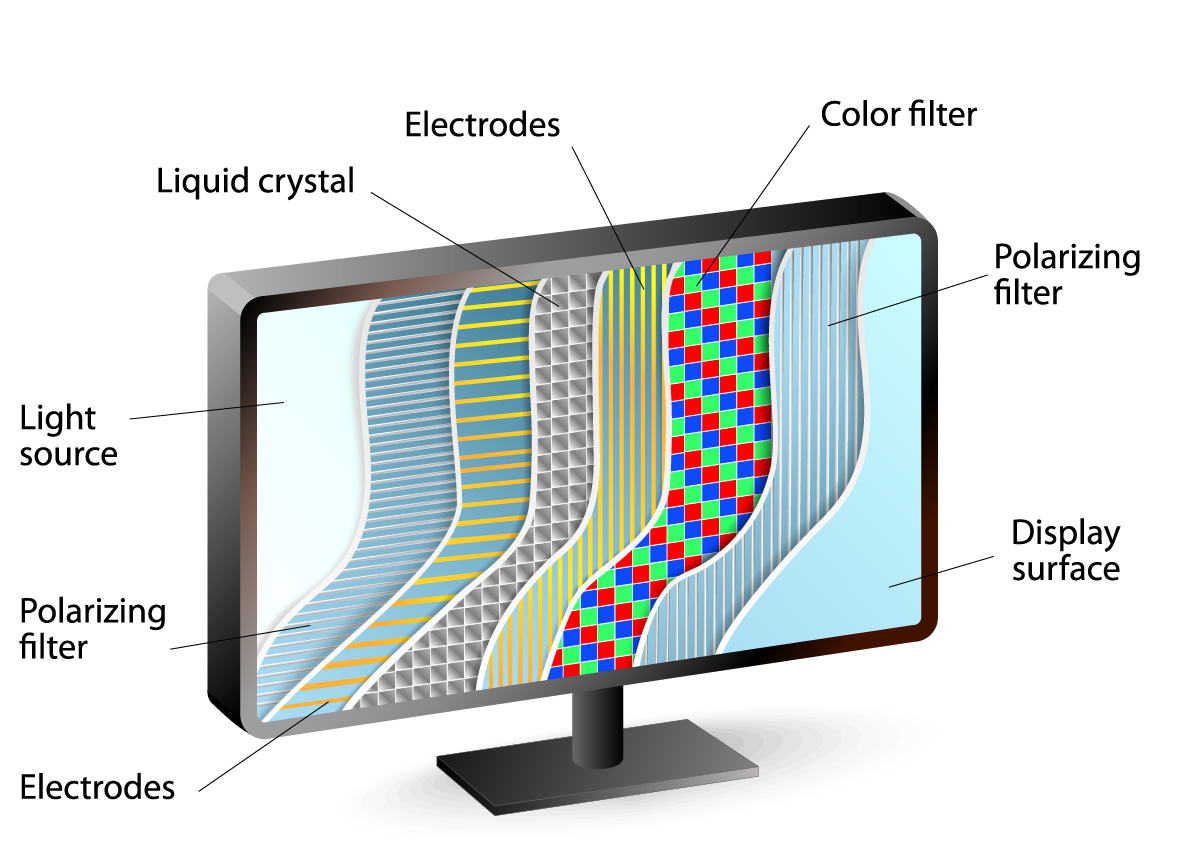
LCD represents Liquid Crystal Display. As you may have realized LCDs have been around for something reasonable of time and deservingly so. An LCD is composed of some fluid gems that get enlightened by a fluorescent backdrop backlight.
Today in this article, we are trying to bring you more information about LCD, OLED, and AMOLED screens.
Table of Contents
There are mainly two types of LCDs used on smartphones:
TFT LCD: Famous among cell phones, gives preferred picture quality over earlier generation LCDs yet winds up consuming a ton of power consequently diminishing battery reinforcement.
IPS LCD: It is moderately costly and is typically found on very good quality gadgets, gives better review points, and devours less power than TFT LCDs.
Advantages:
Nearly better display under direct daylight.
Predictable utilization of power, not influenced by color on display.
Disadvantages:
Blacks will, in general, seem grey, need contrast.
Nearly lower picture quality.
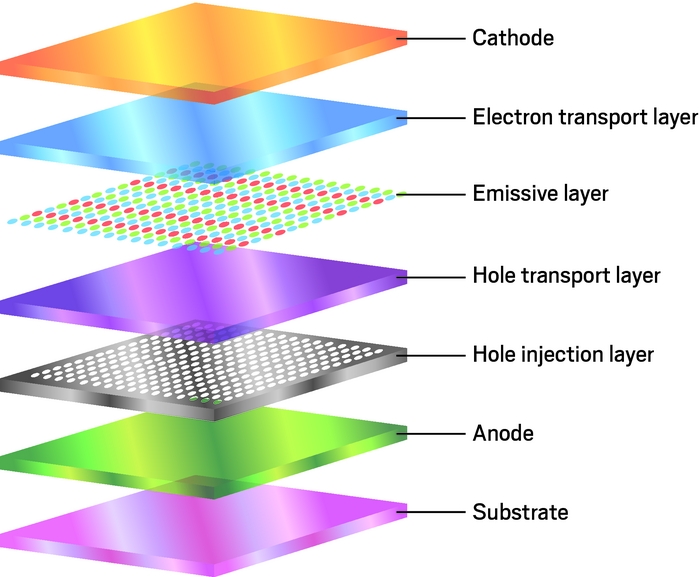
Organic Light-Emitting Diode (OLED): It is a thin-film that shows innovation that contains OLED, a natural material that radiates light when the current is gone through it. OLEDs show much better blacks and devour less force while showing hazier tones since OLEDs are consistently off except if zapped independently.
Read More: ASUS Vivobook F510UA Review: Features, Specifications & Prices
There are primarily two types of OLEDs:
PMOLED: Passive Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diode utilizes a basic control plot in which each line in the display is controlled consecutively. PMOLEDs are modest and straightforward to create, yet they are not effective, and their lifetime is generally less. They are regularly utilized in more modest showcases of up to 3 inches.
AMOLED: Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diode is mostly determined by a TFT, which contains a capacity capacitor and can subsequently uphold bigger showcases. AMOLED shows have no size limitations and work on similar major standards as an OLED display.
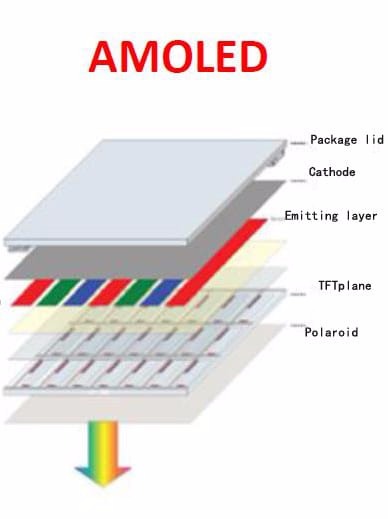
Active Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode (AMOLED): AMOLED or Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diode is, to a greater extent, a stage forward from the OLED show innovation. TFT innovation is critical to AMOLED. A functioning system of OLEDs is saved on a TFT plane that initiates getting electrical flows. These TFT clusters switch for every pixel and contain the capacity capacitor that considers bigger displays.
Schematic of an active-matrix OLED display: Regularly an AMOLED show would comprise of two TFTs at every pixel, one to begin and stop the charging of capacity capacitors and the other to give a consistent voltage or current to the pixel
Advantages:
Thinner and more adaptable than LCDs.
Quicker refresh rate.
No limitation on the size of the display.
Higher contrast ratio.
Burns-through less power when more obscure tones are shown.
Disadvantages:
No backlight hence poor display under direct sunlight.
Consumes more power when brighter colors are displayed.
Organic material is used. Hence it has a shorter lifetime.
No backdrop illumination henceforth helpless presentation under direct daylight.
Burns-through more force when more splendid tones are shown.
The natural material is utilized; thus, it has a more limited lifetime.