The normal CPU temp while gaming should be between 75 Celsius and 80 Celsius (Between 167 and 176°F). As such, the optimal CPU gaming temperature is about 80° Celsius (176°F).
The normal graphics processing unit (GPU) temperature range is between 65 degrees Celsius and 75 degrees Celsius (149-167°F). However, the leading GPU models are capped at around 95°C (203°F).
The normal CPU temp while gaming range for modern central and graphic processors has become slightly lower than in the past, associated with more complex technologies and more nuanced manufacturing processes. Simultaneously, the threshold values for different models and manufacturers are different, so it is impossible to give anyone a universal value and call it the “normal CPU temp while gaming.” Let’s get it right.
Throughout this guide, you will learn what causes the GPU and CPU temperature to rise and how the high temp affects performance. You will also learn how to ascertain the current CPU and GPU temperature while gaming and what you can do to lower the temperature.
Table of Contents
How to monitor CPU and GPU temperature?
There are two ways to monitor CPU and GPU temperature.
Option 1: Enter the BIOS and look for a specific section
When loading, we go to the BIOS by pressing F2 or Del (keys are different for different manufacturers). There is a System Health tab that contains readings from various sensors, including processor temperature.
Second option: using special utilities
Install the program AIDA64 or CPU-Z or HWMonitor. There are many similar options. All of these utilities display detailed information about the computer and information from the sensors and not forget the temperature of the processor. To determine if your CPU or GPU temperature is within the normal range, you must first know the actual temperature reading on your gaming computer. Below are three main methods you can use to find the temperature of your GPU and CPU at any given time:
Via UEFI / BIOS
The Basic Input / Input Output System (BIOS) runs in your operating system’s background and introduces the firmware settings. On the latest operating systems, such as Windows 10, the BIOS is replaced with an updated version called the Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI).
However, the performance of UEFI and BIOS is more or less the same. You can use the BIOS or UEFI to find out the GPU or CPU temperature depending on the OS version you are running. On older versions of Windows, press F12, F2, Esc, or Delete on the Startup screen to access the BIOS.
How to access UEFI in Windows 10
In Windows 10, you can access UEFI from your Windows menu. To do this, open the Windows menu in the lower-left corner of the screen. Then you have to hold down the power and shift keys. You must then select the Restart option.
The computer then displays a series of menus. Navigate to Troubleshoot> Advanced Options> UEFI Firmware Settings. Finally, select Restart. The PC will now boot into the UEFI menu, from which you can read the current CPU / GPU temperature.
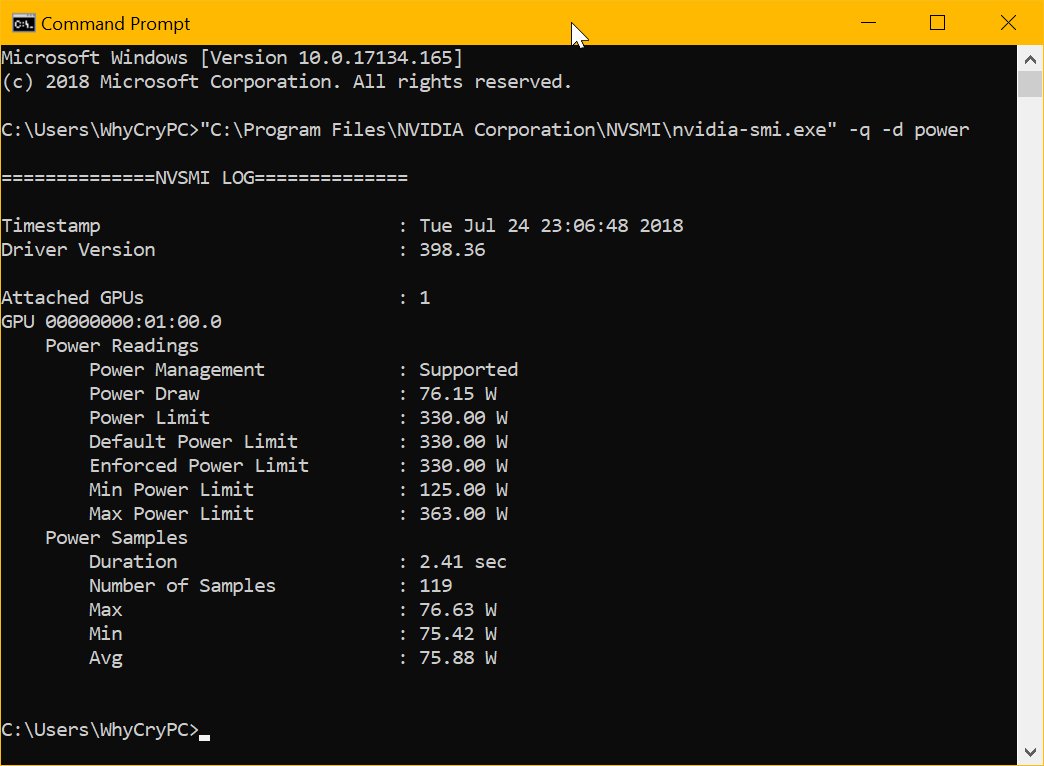
Use the Nvidia-SMI tool.
It is a built-in tool for Nvidia graphics cards. It monitors to monitor GPU status and usage, including current GPU temperature. All you have to do is run Nvidia-smi.exe in CMD. To do this, press the Windows + R key combination and press Enter to start the Run dialog box.
Navigate to the location of Nvidia-smi.exe on your gaming and click on the app. (Change “C” according to your drive letter)
- C:\Program Files\NVIDIACorporation\NVSMI\nvidia-smi.exe
This operation displays a table with parameters such as GPU temperature, graphics card model, graphics card model, and performance status.
Use the CPU Utility Tool
If you are using an Intel or AMD CPU, you can use popular CPU temperature monitoring devices to read the current CPU template on your gaming computer. In this case, you can download and install utility tools such as Raison Master for AMD CPUs or Intel Extreme Tuning Utility for Intel CPUs.
In addition to giving you accurate CPU temperature readings, running such devices will allow you to see and improve CPU performance.
Should GPU and CPU temperature be different?
The central processing unit (CPU) and graphics processing unit (GPU) are two different components on your gaming computer. Although the two components work together during gaming, their temperature readings may be different.
Is there a difference between CPU and GPU temperature? GPU is a specialized processor that speeds up repetitive and intense tasks such as reading high-resolution videos and images. Both of these are used more intensely, which heats up more.
Read More: Fix Windows Audio Device Graph Isolation High CPU Usage Issue
The Average CPU Temp While Gaming by Processor Model
Different CPU manufacturers such as Intel and AMD have developed different processor models for different computer applications during gaming. A typical CPU gaming temp varies from one processor model to another. However, for customized gaming PCs with high-quality cooling features, you should expect a temperature reading of up to 50 degrees Celsius (122 F).
For more powerful laptops, the CPU temperature can rise to 75 degrees Celsius (167 ° F) during intense use. This can be due to a lack of space and no cooling options. If the PC is pushed to its limit, the CPU temperature will rise above 80 C (176 F).
While this may not cause an alarm, you should not allow the temperature to remain at this level. To understand the safe temperature for your CPU, you should study the maximum and average temperature for a particular CPU model, as shown below:
| Processor Model | Maximum CPU Temperature | Normal CPU Temp Range |
| Intel Core i3-7350K | 100°C | 45°C to 60°C |
| Intel Core i5-6600K | 72°C | 42°C to 53°C |
| Intel Core i5-7600K | 100°C | 45°C to 65°C |
| Intel Core i5 4690K | 74°C | about 60°C |
| Intel Core i5-4670K | 72°C | 47°C to 60°C |
| Intel Core i5-3570K | 67°C | 50°C to 62°C |
| Intel Core i7-7700K | 100°C | 50°C to 70°C |
| Intel Core i7-4790K | 73°C | Below 70°C |
| Intel Core i7-6700K | 72°C | 52°C to 70 °C |
| Intel Core i7-3770K | 72°C | 55°C to 65°C |
| Intel Celeron | 73°C | 67°C to 85°C |
| Intel Pentium Pro | 85°C | 75°C |
| Intel Core 2 Duo | 105°C | 45°C to 55°C |
| AMD A6-6400K | 70°C | 49°C to 57°C |
| AMD A6-7400K | 70°C | 45°C to 57°C |
| AMD A6-5400K | 70°C | 45°C to 55°C |
| AMD A10-6800K | 74°C | 50°C to 55°C |
| AMD Athlon FX | 70°C | 45°C to 60°C |
| AMD Athlon 64 | 78°C | 45°C to 60°C |
| AMD Athlon 64 X2 | 78°C | 45°C to 55°C |
| AMD Phenom X4 | 62°C | 50°C to 60°C |
| AMD Phenom II X6 | 62°C | 45°C to 55°C |
| AMD Opteron | 69°C | 54°C to 60°C |
How does high CPU temperature affect performance?
Any above the maximum temperature listed in this table is considered overheating. The CPU warms up every time without causing serious problems. If this continues for a long time, high temperatures can affect CPU performance.
When your gaming computer’s GPU or CPU overheats, it automatically starts throttling its performance in an attempt to lower the temperature. This can affect the refresh rate (FPS) of the display or reduce the Fidelity of the images as you play.
Again, overheating can cause the affected components to deteriorate over time. To resolve the issue, the CPU and GPU must take the necessary steps to reduce the temperature.
GPU types
AMD and Nvidia, however, unlike central processors, these companies make ready-made video cards rarely independently – this is done by partner manufacturers who install different cooling systems on the cards.
However, this fact does not change the upper limit of the AMD Radeon and Nvidia GeForce GPU’s operating temperature, which is about 95 C. In this case, as a rule, AMD cards overheat due to the design features of the processor. However, in most processors, in most cases, the loaded GPU’s operating temperature should not exceed 85 C. The problem is that the cooling systems installed on video cards are very different, so the average temperature is also different.
Two main types of active cooling systems are installed for video cards: open fans and centrifugal cooler in a closed box. The first is the most common cooling option used in any class of video cards. One, two, or three fans run the air through a radiator connected to the card. In this case, adequately installed case fans contribute to the high-quality cooling of the video card.
The second type of cooling system is installed in high-performance video cards; a turbofan that sucks in cold air drives it through the radiator and blows hot air through the grills at the back of the case. Such cards’ temperature depends on the currents maintained by the case fans, which usually operate at higher temperatures.
Almost all modern video cards have a custom fan speed control system. This means that until a specific temperature is reached, generally up to 30-40 C, the fans do not rotate at all or rotate at low speeds. This is to reduce power consumption and reduce system noise when idle. However, in this case, the unloaded card is hotter than the one with the running fan.
Also Read: What is AMD GPU Scaling in Settings for AMD Graphics Driver?
Final judgment
Typical CPU temperatures range from 167 to 176 degrees Fahrenheit. In regular use, the GPU temperature should be between 149 and 167 F. If used for more intensive applications such as gaming; the CPU temperature is likely to rise beyond this limit.
If left untreated, overheating of the CPU can affect its performance and image quality. Overheating will cause the components to deteriorate over time. With this guide, you can lower the CPU temperature and keep it acceptable while playing games.