How To
‘This PC can’t be upgraded’ error while upgrading to Windows 10?...
You might encounter this error for various reasons, including incompatible hardware or software, insufficient disk space, or corrupted system files that stop you from...
Discord
Business
Login Process
Minecraft
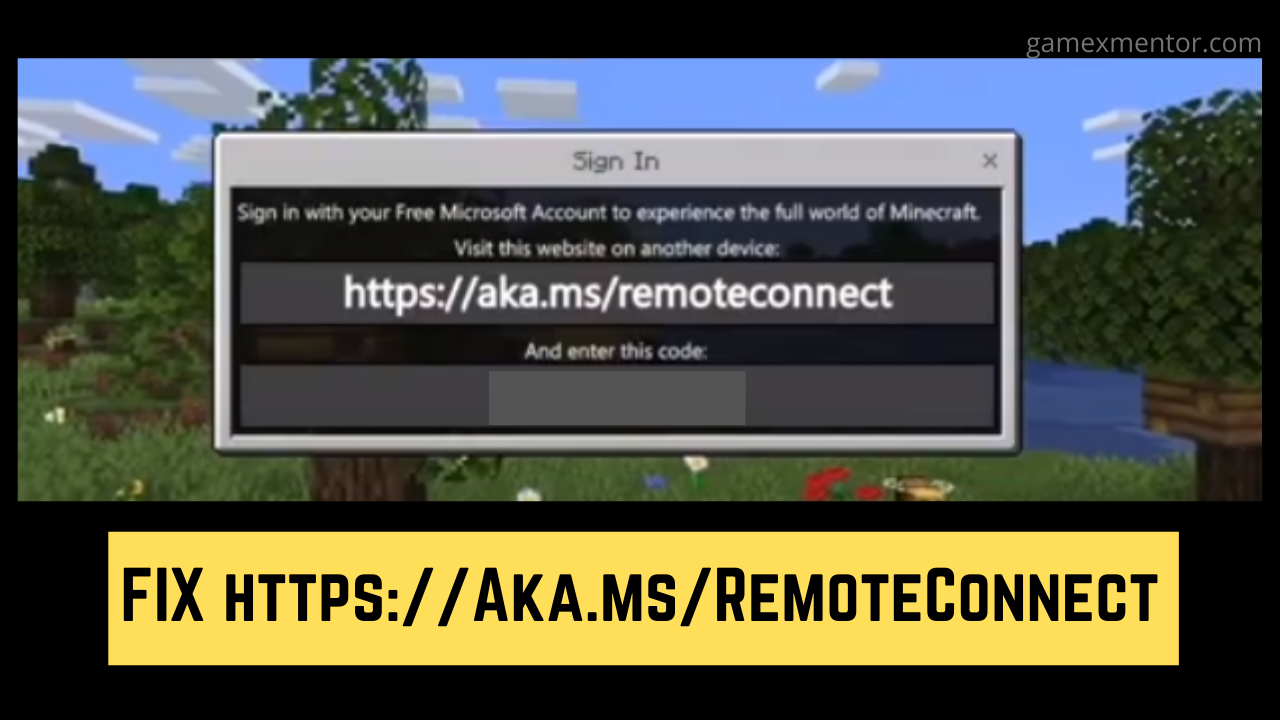
Https://Aka.Ms/RemoteConnect- Minecraft Remote Connect on Xbox, Playstation And Nintendo
Are you experiencing difficulty while attempting to sign in to your Microsoft account, The https://aka.ms/remoteconnect issue is normal for a great deal of Minecraft...
Essential Factors to Consider When Choosing a Minecraft Server
Minecraft is one of the world’s most popular online games. Sadly though, many online servers are plagued by griefers and trolls. If you aren’t...